Carbon steel flanges are critical components in piping systems, ensuring secure connections and reliable performance across various industrial applications. Their dimensions are governed by international standards to guarantee compatibility and safety. This article provides a comprehensive overview of carbon steel flange dimensions, focusing on key standards, parameters, and selection considerations.
Key Standards for Carbon Steel Flange Dimensions
Carbon steel flange dimensions are defined by several globally recognized standards, each with specific applications:
ASME B16.5 (ANSI)
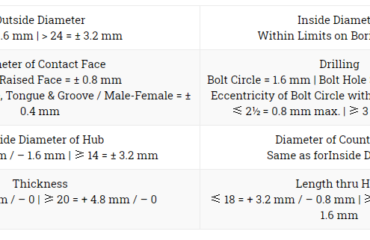
Widely used in North America, this standard covers flanges from NPS 1/2 to 24 (DN 15 to 600) with pressure classes ranging from 150 to 2500. Key dimensions include outer diameter (OD), bolt circle diameter (BCD), bolt hole diameter (BHD), and flange thickness (T). For example, a Class 150 flange with NPS 2 has an OD of 98.6 mm, BCD of 65 mm, and thickness of 15.7 mm.
DIN 2501
The German standard applies to flanges in metric sizes (DN 10 to DN 1200) with pressure classes PN 6 to PN 320. It specifies detailed dimensions like flange diameter (A), bolt circle diameter (D1), and number of bolts (N). For instance, a DN 50 PN 16 flange has an A of 165 mm, D1 of 125 mm, and 4 bolt holes of 18 mm.
JIS B2238/B2239
Japanese Industrial Standards cover flanges in sizes from DN 10 to DN 600 with pressure classes 5K and 10K. The dimensions include flange outer diameter, bolt hole pattern, and thickness. A DN 100 JIS 10K flange has an outer diameter of 210 mm and 8 bolt holes of 19 mm.
GB (Chinese National Standards)
These standards, such as GB 9119.2-88, define dimensions for flanges from DN 15 to DN 2000. For example, a DN 50 GB flange with PN 16 has an outer diameter of 160 mm and 4 bolt holes of 18 mm.
Critical Dimensions and Their Significance
Flange dimensions are categorized into primary and secondary parameters:
Nominal Pipe Size (NPS) or DN
This indicates the pipe diameter the flange connects to. NPS uses inches (e.g., 1/2″), while DN uses millimeters (e.g., DN 15). Flanges must match the NPS/DN of the connected pipes for proper fit.
Outer Diameter (OD)
The overall size of the flange, influencing space requirements and compatibility. Larger OD flanges are used in high-pressure applications to distribute stress evenly.
Bolt Circle Diameter (BCD)
The diameter of the circle formed by the bolt holes. Misalignment in BCD can lead to installation issues. For example, a Class 300 flange with NPS 4 has a BCD of 115 mm.
Bolt Hole Diameter (BHD) and Quantity
Determines the size and number of bolts needed. Higher pressure classes require larger bolts. A DIN PN 40 flange may have 8 bolt holes of 22 mm.
Flange Thickness (T)
Varies with pressure rating. Thicker flanges (e.g., Class 2500) are designed for high-pressure systems. For instance, a Class 1500 flange with NPS 2 has a thickness of 40.9 mm.
Sealing Face Type
Options include Raised Face (RF), Flat Face (FF), and Ring Joint Face (RJ). RF flanges are common for general use, while RJ is preferred in high-pressure, high-temperature applications.
Pressure and Temperature Ratings
Carbon steel flanges have specific pressure-temperature ratings based on material and design. For example:
ASTM A105 flanges in Class 150 can handle up to 285 psi at 100°F (38°C) but reduce to 50 psi at 1000°F (538°C).
DIN PN 16 flanges made of carbon steel are rated for 16 bar (232 psi) at ambient temperatures but decrease with higher temperatures.
Selection Considerations
Choosing the right flange dimensions involves evaluating:
Application Requirements: Pressure, temperature, and fluid type. High-pressure systems (e.g., oil refining) require thicker flanges with larger bolts.
Standards Compliance: Ensure compatibility with existing piping systems. Mixing ANSI and DIN flanges requires adapters due to differing bolt patterns and measurements.
Material Compatibility: Carbon steel (e.g., ASTM A105) is suitable for general use, while low-temperature applications may require ASTM A350 LF2 for enhanced toughness.
Installation Practices: Proper bolt tightening torque (e.g., ASME B16.5 specifies torque values based on flange class and bolt size) ensures leak-free connections.
Industry Applications
Carbon steel flanges are widely used in:
Oil and Gas: High-pressure pipelines (e.g., Class 900 flanges) for transporting hydrocarbons.
Power Generation: Steam systems requiring flanges with high-temperature resistance.
Water Treatment: Large-diameter flanges (DN 600+) for municipal water supply networks.
Conclusion
Accurate carbon steel flange dimensions are vital for safe and efficient piping system operation. Adhering to standards like ASME B16.5, DIN 2501, and JIS ensures compatibility, while proper selection based on pressure, temperature, and material guarantees reliability. By understanding these dimensions and their applications, industries can optimize performance and minimize maintenance costs.
 Language
Language Espanol
Espanol English
English Italian
Italian عربى
عربى
 Skype: chinamaker99
Skype: chinamaker99  Tel: 86-316-5120812
Tel: 86-316-5120812  Email:
Email:  Whatsapp:
Whatsapp: