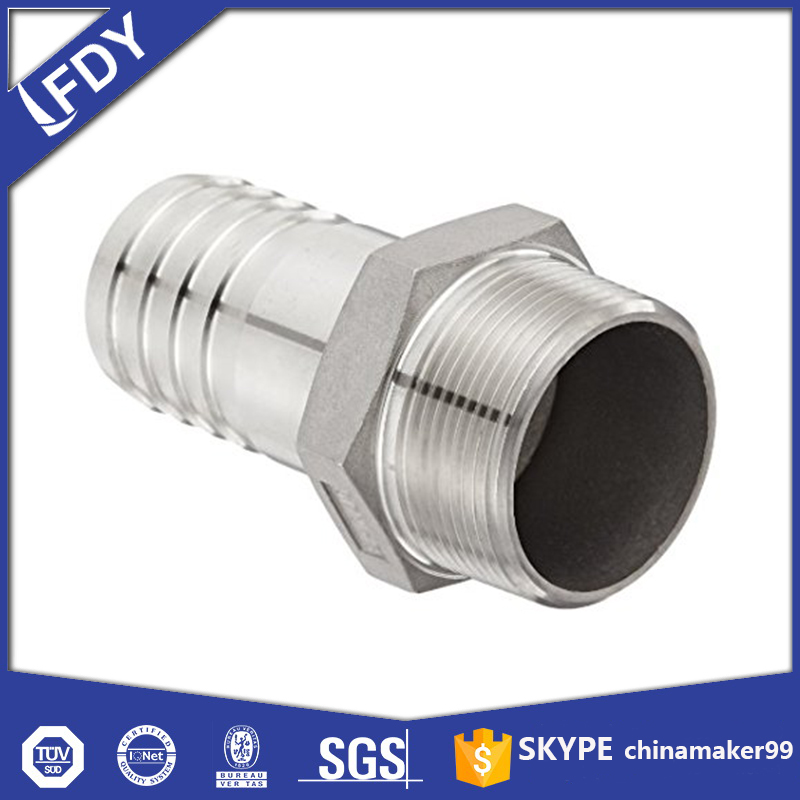
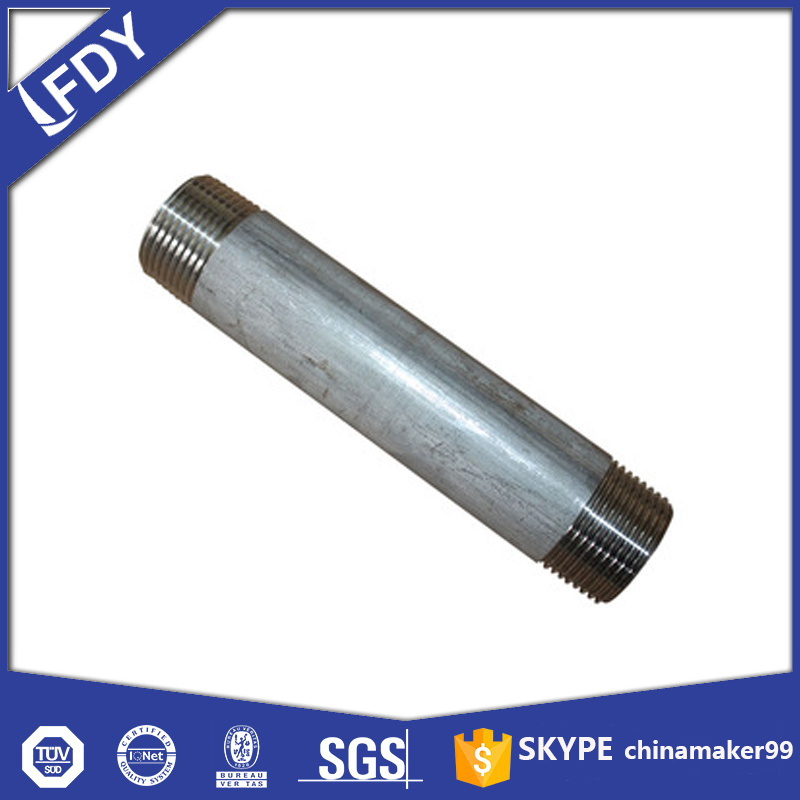
Steel nipple fittings are short, cylindrical pipe components with threaded ends, designed to connect pipes, valves, or other plumbing parts in industrial, commercial, and residential systems. Unlike longer pipes, their compact size makes them ideal for bridging small gaps between fixtures, ensuring a secure and leak-free flow of fluids or gases. Their durability and versatility have made them a staple in plumbing and piping networks worldwide.
One of the key advantages of steel nipple fittings is their strength and resistance to wear. Made from materials like carbon steel, stainless steel, or alloy steel, they can withstand high pressure, temperature fluctuations, and exposure to corrosive substances—depending on the steel type. For example, stainless steel nipples are often used in food processing or pharmaceutical facilities, where hygiene and resistance to chemical cleaners are critical. Carbon steel nipples, on the other hand, are common in industrial settings like manufacturing plants, where cost-effectiveness and high-pressure tolerance are priorities.
Steel nipple fittings come in various types to suit different installation needs. Threaded nipples are the most common, with male threads on both ends that screw into female-threaded pipes or fixtures. They’re easy to install and require no welding, making them a popular choice for quick repairs or temporary setups. Welded nipples, by contrast, have unthreaded ends that are welded directly to pipes, offering a more permanent and high-strength connection—ideal for high-pressure systems like oil and gas pipelines. Another type is the close nipple, which has threads extending almost to the center, leaving little to no gap between connected parts, while long nipples have a longer unthreaded section in the middle, useful for spanning larger spaces.
Proper selection of steel nipple fittings is essential to ensure system safety and efficiency. First, consider the application’s pressure and temperature requirements. A fitting designed for low-pressure water lines may fail in a high-pressure steam system, leading to leaks or bursts. Second, match the fitting’s material to the fluid or gas being transported. For instance, if the system carries saltwater (like in marine applications), a corrosion-resistant stainless steel nipple is necessary to prevent rust and degradation. Third, check the thread size and type—different regions use different standards (such as NPT in North America or BSP in Europe), so mismatched threads can cause leaks or damage to components.

Installation and maintenance also play a role in maximizing the lifespan of steel nipple fittings. During installation, avoid over-tightening, as this can strip threads or warp the fitting, compromising the seal. Using thread sealant or Teflon tape can help create a tighter seal and prevent leaks. Regular inspections are important too—look for signs of corrosion, cracks, or loose connections, especially in harsh environments. Replacing worn or damaged nipples promptly can prevent larger system failures and reduce maintenance costs over time.
In conclusion, steel nipple fittings are a simple yet essential component in piping systems, offering flexibility, strength, and reliability. By understanding their types, material options, and selection criteria, users can ensure they choose the right fitting for their specific application, leading to safer and more efficient operations. Whether in a home plumbing system or a large-scale industrial facility, these small components play a big role in keeping fluids and gases flowing smoothly.
 Language
Language Espanol
Espanol English
English Italian
Italian عربى
عربى
 Skype: chinamaker99
Skype: chinamaker99  Tel: 86-316-5120812
Tel: 86-316-5120812  Email:
Email:  Whatsapp:
Whatsapp: